Designed to be worn as a convenient part of a miner’s regular protective equipment, the PDM detects worker exposure to respirable dust in real time. Extensive testing has shown the PDM to be an effective tool for measuring miners’ dust exposure. The real-time data display empowers miners to reduce their work exposure to coal mine dust. Now new software makes it easier to transfer, secure and analyze data from the device.
The PDM is manufactured commercially by Thermo Scientific. Included with the device is WinPDM, a software application for configuring the device settings. This software is also capable of producing a Comma Separated Value (CSV) file from PDM data, which is then exported into other applications for processing. Spreadsheet applications such as Microsoft Excel can be used for simple analysis of the data; however, translating data from multiple instruments into summary reports requires substantial effort. In addition, tracking information for multiple days, specific occupations, groups of instruments, and other such scenarios becomes a complicated endeavor.
To address these issues, NIOSH has developed new Personal Dust Monitor Management Studio (PDMMS) software (Figure 1). The PDMMS is designed to allow the average user on an individual personal computer to analyze data from Personal Dust Monitor devices. The user-friendly PDMMS does not require a connection to the Internet or to a network database. No specialized computer skills are needed to analyze the data. The PDMMS simplifies and manages data from the PDM, processes the data, produces various standardized reports, and stores secure files. Reports are presented in easy-to-read graphical form. The software aids in reporting data uniformly across the industry and ensures the data is in a format both readily accessible for mine personnel and convenient for archiving. The database file structure is designed to be compatible with larger company-wide database management systems. By default, the system uses a local database to store data, however it can also be configured to use a shared network database. The PDMMS also offers security, file validation, data acquisition, reporting and file management features not available in WinPDM.
Figure 1
Files can be imported into the PDMMS directly from the PDM, or from other CSV files. When the PDM is connected for downloading data, the PDMMS program automatically searches the device and downloads any files not already in the local database. The PDMMS allows multiple devices to be connected to a common serial bus and downloaded with a single action. The user can select specific files to add to the database by using the advanced download option, and also has the option to input production data and field notes for each file.
Files secured with digital signatures travel with exported CSV files that originate from a PDMMS download. This ensures the authentication for those files is tamper-free and uncorrupted. Data from PDMMS can therefore be imported into another installation of PDMMS while maintaining authentication and validation. CSV files from other sources can also be imported to the database and validated, but, lacking digital signatures, they cannot be authenticated.
Nearly any type of report can be generated from the data stored in the PDMMS. The software provides a selection of pre-formatted, pre-defined reports as well as the ability to customize more advanced reports. Simple, user-friendly processes such as selecting options from drop-down menus generate basic reports and display numeric and graphical data in easy-to-read formats.
Individual reports contain data from individual PDMs, selected by user identification and date. These reports contain end-of-shift data, all information programmed in the PDM, and summary graphs of exposure data, flow parameters and tilt movements of the device.
Foreman reports contain data from all PDMs worn by miners on a specific mechanized mining unit (MMU). These reports are designed to show the foreman the relevant information from each PDM worn in his section at a glance. They show end-of-shift data for each worker by occupation, graphs of exposure over time, and cumulative weekly dose exposure by wearer on a running seven-day period basis. These reports also display the number of samples at less than 50% of permissible exposure level (PEL), at 51-100% of PEL, and at greater than PEL, by day and by week. They also show the number of authentic and valid samples by day and by week. When viewed on the PDMMS system, specific individual files may be recalled with a single key stroke for closer examination.
Mine manager reports show daily and weekly results from the foreman reports and contain summary data for all MMUs and all shifts. These reports display the number of samples at less than 50% of PEL, at 51%-100% of PEL, and at greater than PEL, by day and by shift. Summary exposure graphs by week, month and year are shown, as are the number of valid and secure samples by day and week. Production for each MMU is included.
Company reports contain summary data for all mine manager reports. These reports show overall summary exposure graphs for all mines owned by a company. These are displayed by year, and show the number of authentic and valid samples by month.
An additional “drill down” feature is available for foreman reports, mine manager reports and company reports, whereby the user can click on a count value to view the list of samples comprising that value.
Signature reports display the signature statuses of all samples within a time period selected by the user to allow easy observation of which reports are authentic, secure and valid. These reports indicate for each sample whether or not the data came from the original PDM source files, and whether the data is valid according to the selected parameters.
Import reports provide information on data from dust samples imported on a date selected by the user. In addition to showing lists of samples imported on the selected date, these reports also allow the user to append notes to individual samples.
The Advanced Mode Button
Advanced reports allow the user to compare multiple samples side by side. This is accomplished with a simple two-step process. The user first selects the samples to be analyzed, and then selects the parameters to compare.
Samples are located in the database for analysis using either the Browse or Search functions, conveniently indicated by tabs. Browse presents the user with a “tree” view, similar to the view produced by Microsoft Windows File Explorer, in which samples are displayed chronologically. The user locates samples by year, month and day. The Search function allows the user to locate samples by attributes or properties (Figure 2), such as sample type, validation, date range, certifier, device, mine, company, contractor, MMU, wearer and occupation. For example, a user could search for all continuous miner operator samples from a specific mine, company or MMU over a given range of time periods. Both the Browse and Search functions display lists of the samples located, and samples are added to an analysis list for comparison by way of a simple click.
Figure 2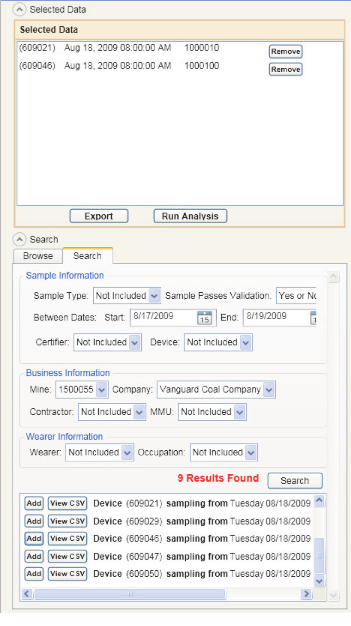
Next, the user selects the attribute to be compared in the report, and the PDMMS graphs the value of that parameter in each sample. Data for each sample are color-coded for ease of identification. The user can “zoom in” to focus on and enlarge areas of the graph for more detail. For engineering analysis, the user can tag time intervals of interest on the graph easily by clicking on the graph to select start and end times, and indicate whether the sample values in the tagged area should be averaged or summed (Figure 3). Multiple data files may be analyzed using the same tags.
Figure 3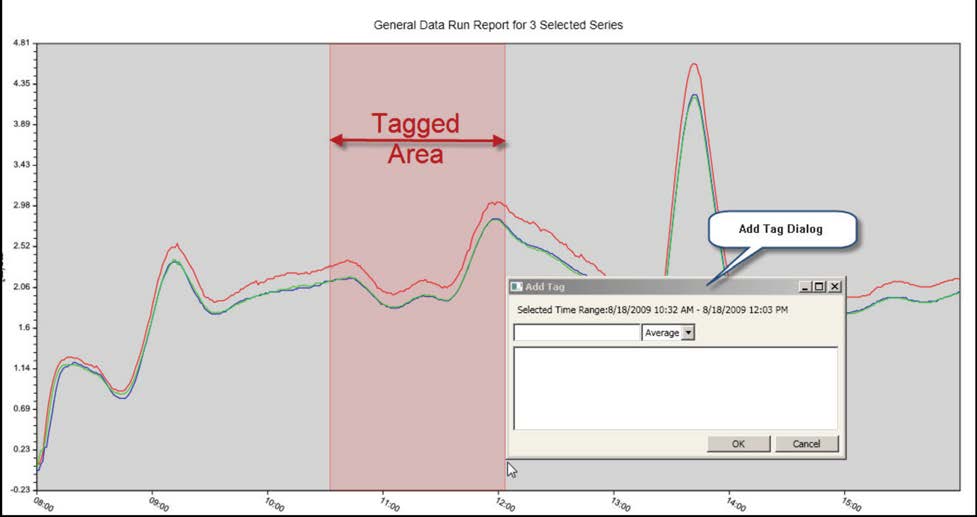
Analysis tags can also generate their own reports to display a list of tags and their associated averages or sums (Figure 4).
Figure 4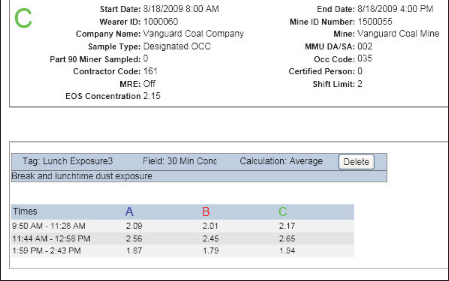
Other PDMMS Features
The first level of security the PDMMS offers is login authentication, so password protection can restrict program access to authorized personnel only. Additionally, the PDMMS adds an important data authentication process to the security features: when a user exports data from the PDM to the PDMMS software, an attached digital signature secures the file. Any changes in the file, including changes to the raw data, will invalidate the signature. Files with intact signatures can be authenticated as original data directly from the PDM, generating confidence in the veracity and trustworthiness of the data.
The PDMMS software reads and reports errors detected by the individual sensors in each PDM instrument. The program is also capable of comparing data from multiple sensors to determine if a sample is valid, establishing further confidence in the data and reducing the need for subjective interpretation of results. The database may also be used to perform historical comparisons of exposure patterns and to flag unusual patterns that may warrant investigation. File validation parameters are subject to updating and revision based upon user experience with the PDM.
The PDMMS simplifies file management. As previously noted, the system is designed to run on an individual PC, without requiring a connection to the Internet or to a mainframe or network database. Data can be exported in CSV format for analysis in programs such as Microsoft Excel. All reports can be printed on any installed printer or the user can save the report as an XML Paper Specification (XPS) file or a Portable Document Format (PDF) file. Digitally signed files can be transferred to other PDMMSs for display, analysis and verification. These secured CSV files can be imported into a mine’s database network. CSV files without digital signatures can also be imported, although these files will not be authenticated.
The PDMMS represents a significant advance in capabilities over previous software used to access PDM data files. The PDMMS has been designed to allow the average PC user to easily access and present data in formats that allow miners and others to make the most of the opportunities presented by the PDM. Because the software secures, authenticates and validates data, reports are trustworthy and verifiable. Users can choose from a variety of basic, pre-formatted reports, or generate more advanced reports for specialized purposes. Files are easy to manage and can be exported to other programs for maximum flexibility in user options. By simplifying the data management process, the PDMMS lets users take full advantage of PDM protective technology and ultimately improve miner health. A free copy of the software may be downloaded from http://pdmms.com/downloads.aspx.
Petrice is PDMMS project lead for Emergint Technologies. Jackson also works with Emergint Technologies. Volkwein is a retired research physical scientist formerly with NIOSH-OMSHR.
References
Volkwein J.C., Vinson R.P., Page S.J., McWilliams L.J., Joy G.J., Mischler S.E., and Tuchman D.P., Laboratory and Field Performance of a Continuously Measuring Personal Respirable Dust Monitor, CDC RI 9669, September 2006, 47 pp. Volkwein J.C., Vinson R.P., McWilliams L.J., Tuchman D.P., and Mischler S.E., Performance of a New Personal Respirable Dust Monitor for Mine Use, CDC RI 9663, June 2004.




